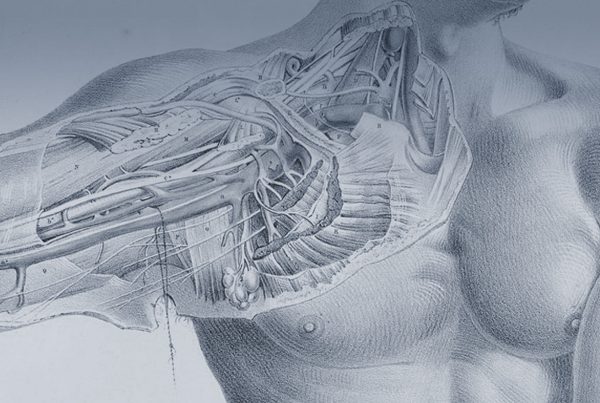
Nerve injury is a complex condition and recovery is difficult to predict and assess. Please see below for a selection of key points as to what we can expect from recovery after nerve injury.
Pain
Pain from damage to skin or bone is common and protects us. Damage to the nerves that sense this injury can cause nerve pain or neuropathic pain. This pain can be very severe.
Paraesthesiae
Paraesthesiae (strange feelings) in a body part affected by nerve injury can be tingling, shooting, electric, hot cold etc., they can be painful and are then called dysthesiae.
Weakness
Often muscles are left not working by nerve injury. This sometimes can be helped to recover but often the power is less and often less controllable and tires easily.
Numbness
The lack of feeling is produced by damage to the nerves that bring feeling to the body part. This can lead to the area being burnt or blistered or damaged.
Rehabilitation
The key factors in nerve injury recovery are time and effort. Recovery is often frustratingly slow – fractures take 6 weeks to heal, sprains maybe 3 months but injury to a major nerve can take years to recover. There is nothing we can do yet to improve the speed of nerve recovery. The controllable factor is effort; the more the patient works on keeping injured body parts supple, works on retraining movement and feeling, the better the end outcome will be. It is very hard to keep working when nothing appears to be improving but it is so important. We wish to help by establishing clear levels of recovery we can expect for a patient to help with this process.
Surgery
In some cases after nerve injury the nerve can benefit from being re-attached or released from scar tissue, new nerves use to bridge a gap or even redirected to a new function. These are the common surgeries to improve outcome after nerve injury in the short term. At a later stage reconstruction can be used if recovery is incomplete to move working tendons and release or stiffen joints to improve function. All of these involve surgery and are specific to the patient’s own needs and injury pattern.